|
Method
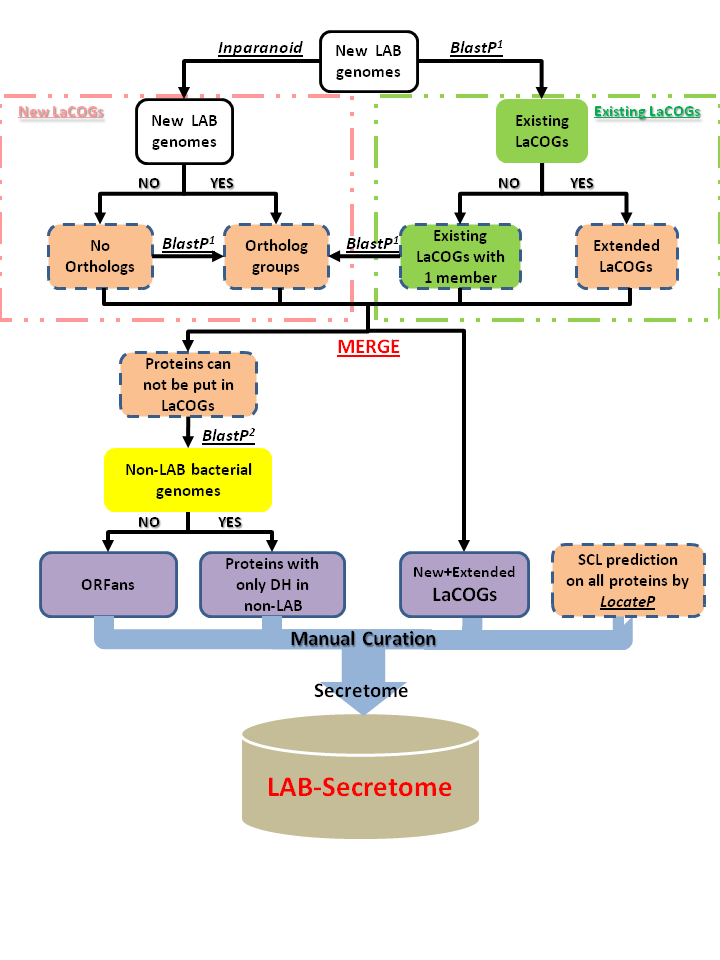
The LaCOGs generated by [1] were extended with newly sequenced genomes by BlastP. In addition, a complete self-to-self Inparanoid [2] search was performed with the chromosomal sequences of the new genomes to identify ortholog groups. The ortholog clusters were used as a basis to perform BlastP searches with proteins that were not yet clustered. Newly made LaCOGs were merged with the extended Makarova LaCOGs. The remaining proteins were Blasted against all completely sequenced bacterial genomes. Those that showed only distant homologs or no homologs were named "distant homologs" and "ORFan"s, respectively.
The above formed clusters were then combined with the SCL prediction made by LocateP [3].
Extra information of protein functional domains and protein feature-specific motifs were detected using Pfam and MEME. The LAB-Secretome database [4] was constructed using MySQL and PHP.
Reference:[1] Makarova KS, Koonin EV (2007): Evolutionary genomics of lactic acid bacteria. J Bacteriol189(4):1199-1208
[2] O'Brien KP, Remm M, Sonnhammer EL (2005): Inparanoid: a comprehensive database of eukaryotic orthologs. Nucleic Acids Res 33(Database issue):D476-480.
[3] Zhou M, Boekhorst J, Francke C, Siezen RJ (2008) LocateP: Genome-scale subcellular-location predictor for bacterial proteins. BMC Bioinformatics 9, 173
[4] Zhou M, Theunissen D, Wels M, Siezen RJ (2010)LAB-Secretome: A genome-scale comparative analysis of the predicted extracellular and surface-associated proteins of Lactic Acid Bacteria. BMC Genomics 2010 Nov 23;11(1):651
|
